Are you looking to start running Google Ads for your ecommerce store but not sure where to begin? Many ecommerce business owners struggle with understanding how to effectively set up and manage Google Ads campaigns. In this guide, let’s explore the best ad types and top strategies, to achieve better results with your campaigns.
Are Google Ads Good for Ecommerce?
Yes, Google Ads are highly effective for ecommerce businesses, enabling retailers to reach potential customers actively searching for products, which significantly boosts conversion opportunities. In 2023, Google’s share of global digital advertising revenue was projected at 39%.
Google Ads’ precise targeting capabilities—based on search queries, location, and past behavior—ensure ads reach relevant audiences, further enhancing conversion rates. WordStream (2024) reports an average conversion rate of 2.81% for ecommerce businesses using Google Search Ads. While this may seem modest, it can lead to substantial revenue, especially when combined with high traffic and optimized campaigns. The platform’s targeting options, from keyword-based ads to retargeting, allow ecommerce businesses to engage the right audience with precision.
Best Ecommerce Google Ads Strategies
Implementing the right strategies is key to maximizing the effectiveness of your Google Ads campaigns for ecommerce. Below are some of the best strategies, each with real-life examples to show how businesses successfully applied them and the positive impacts of their efforts.
#1 Use a Combination of Branded and Non-branded Shopping Ads
Running both branded and non-branded Shopping Ads helps you cover all bases. Branded ads target users who are already familiar with your brand, while non-branded ads reach potential customers searching for similar products. A mix of both ad types ensures you capture users at different stages of the buying funnel.
Real-Life Example: Gymshark, a fitness apparel brand, utilized a combination of branded and non-branded Shopping Ads. They targeted branded keywords like “Gymshark leggings” to capture loyal customers, while also using non-branded terms such as “best workout leggings” to attract new buyers.
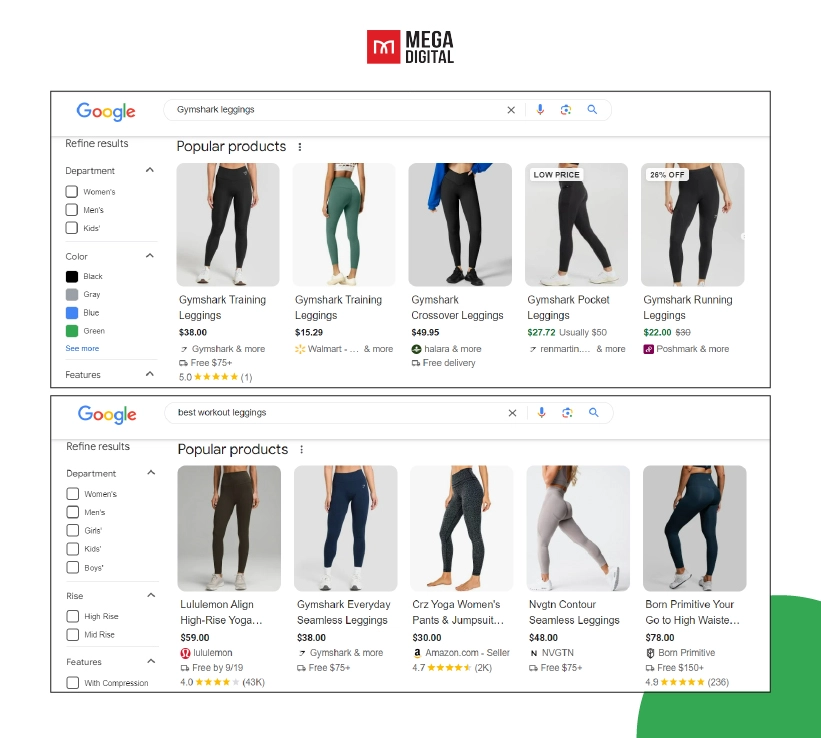
What They Did Well: Gymshark effectively segmented their audience by funnel stage. Branded ads engaged existing customers familiar with their products, while non-branded ads attracted potential customers still exploring their options. This dual approach ensured that Gymshark covered both ends of the buying funnel—brand loyalists and new prospects.
Outcome: The brand saw a 40% increase in overall sales, with a significant boost in conversions from non-branded ads. This approach helped Gymshark capture more market share in a competitive space, demonstrating the importance of targeting both familiar and unfamiliar audiences.
#2 Run Google Retargeting Ad Campaigns
Retargeting ads help you stay connected with potential customers who have visited your site but have not yet converted. As you target these users with personalized ads, you can entice them to return and complete their purchase.
Real-Life Example: Nordstrom, a leading fashion retailer, implemented Google Retargeting Ads to re-engage users who had visited their site but had not completed a purchase. By serving personalized display ads showcasing the exact products customers had viewed, Nordstrom was able to remind potential buyers of the items they showed interest in.
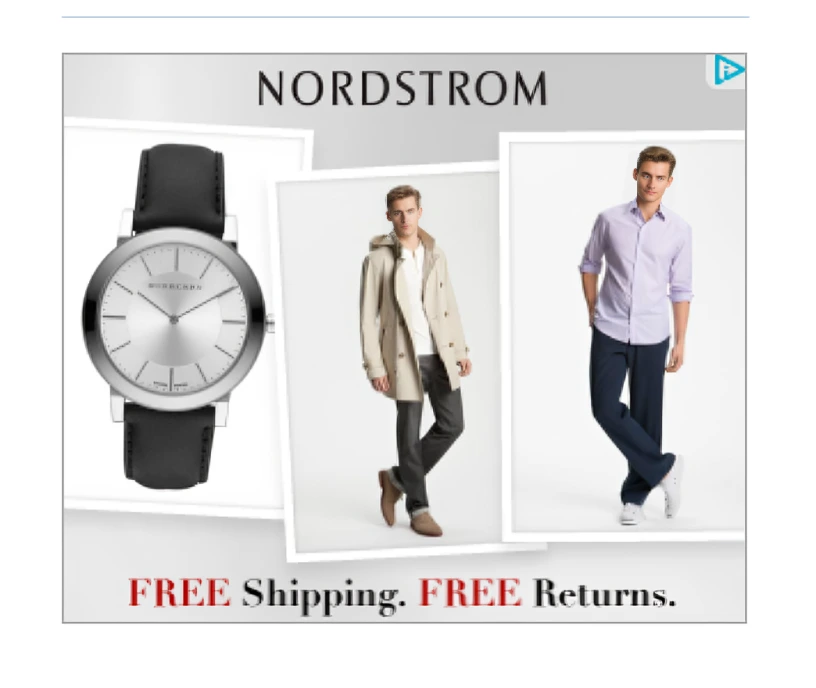
What They Did Well: Nordstrom personalized its retargeting ads by showing users the products they had previously viewed, along with related items. This tailored approach kept the brand top-of-mind and provided customers with additional options to entice them back to complete their purchase.
Outcome: As a result of their retargeting strategy, Nordstrom saw a 60% increase in conversion rates from abandoned cart users. This success highlights the power of retargeting in ecommerce, where re-engaging customers who are already familiar with your brand often leads to higher conversion rates and lower acquisition costs.
#3 Take Advantage of Seasonal Advertising
Catching seasonal trends is crucial for maximizing sales. Seasonal advertising allows you to tailor your campaigns to specific holidays or shopping events, such as Black Friday or Cyber Monday. According to a report by Deloitte, U.S. holiday sales in 2022 reached over $1.39 trillion, highlighting the immense opportunity in seasonal campaigns.
Real-Life Example: Best Buy, a consumer electronics retailer, ramped up its Google Ads efforts during Black Friday and Cyber Monday. They designed specific seasonal campaigns offering limited-time discounts on popular items, which were heavily promoted through Google Shopping and Search Ads.
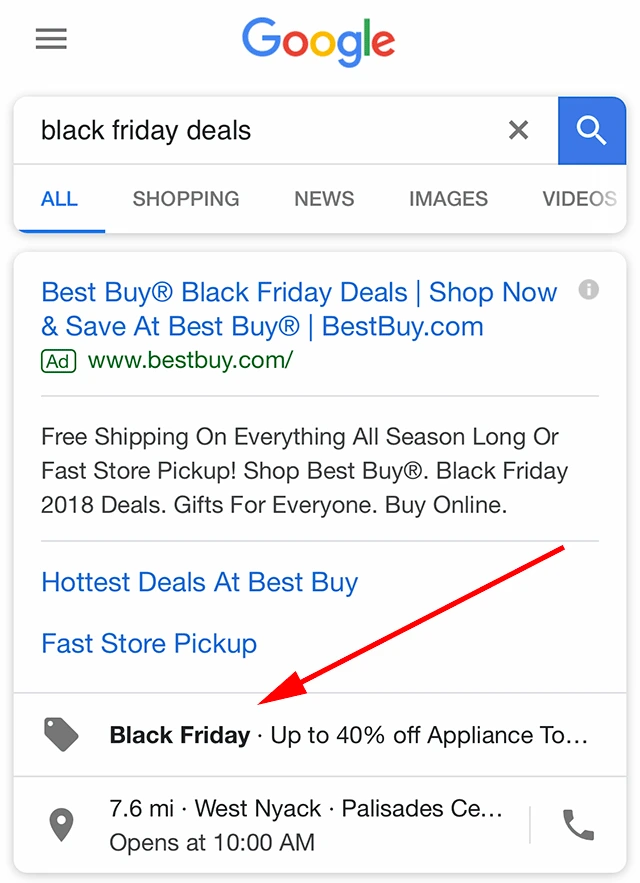
What They Did Well: Best Buy focused on urgency and scarcity in their ad copy by highlighting limited-time offers and exclusive deals available only during these seasonal events. They also tailored their product listings to include seasonal keywords like “Black Friday laptop deals” and “Cyber Monday TV sales.”
Outcome: During the holiday season, Best Buy saw a 45% increase in sales, with 70% of the traffic coming from Google Shopping Ads. Seasonal advertising allowed them to tap into the heightened buying intent during this period, leading to a massive surge in both online and in-store sales.
#4 Utilize Multi-channel Advertising
Using multiple channels, such as Google Ads, YouTube, and Display, increases your visibility and reach. A multi-channel strategy allows you to target users across different platforms, ensuring a cohesive brand experience. YouTube Ads are especially effective for driving engagement, with 70% of people saying they bought a brand’s product after seeing it on YouTube, according to Google.
Real-Life Example: Casper, a mattress company, adopted a multi-channel advertising strategy combining Google Ads, YouTube, and Display Network to increase brand visibility. By running search ads for high-intent queries like “best mattress for side sleepers” while simultaneously using YouTube ads to tell their brand story, Casper was able to reach potential customers at different stages of their buying journey.
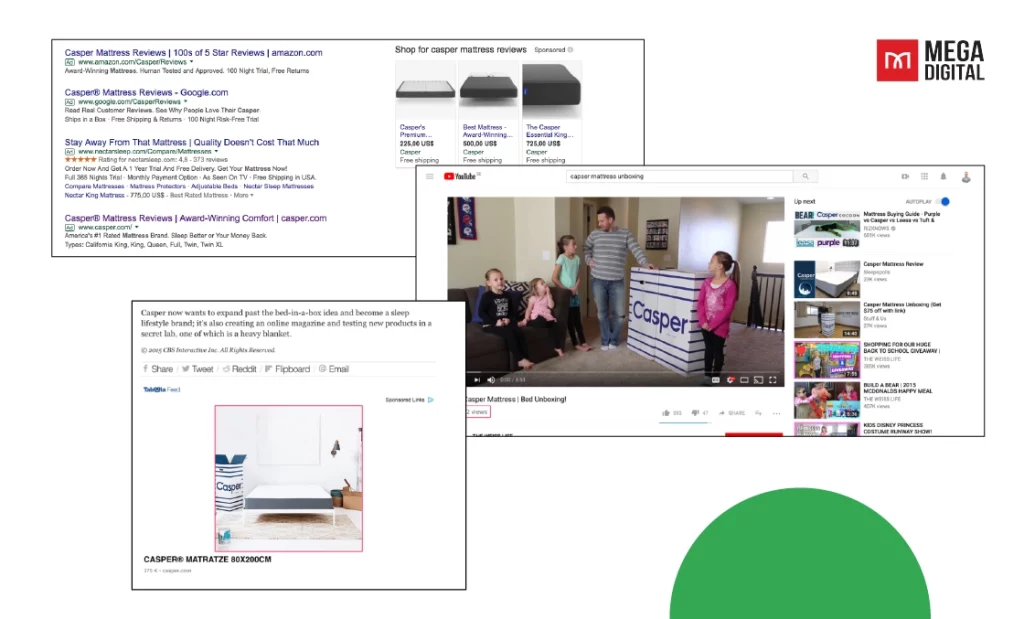
What They Did Well: Casper effectively utilized YouTube for awareness and search ads for conversions. They also used retargeting display ads to keep their products top-of-mind for visitors who hadn’t yet made a purchase. This cohesive experience across multiple platforms ensured they captured attention and conversions at every step of the customer journey.
Outcome: Their multi-channel approach led to a 50% increase in overall website traffic and a 25% increase in conversion rates. The combination of video and search ads allowed them to appeal to both informational and transactional queries, maximizing their reach and driving sales.
#5 Target Competitor Keywords
Targeting competitor keywords is a smart tactic to capitalize on your rivals’ traffic. When you bid on competitor terms, you can appear alongside their products in search results, potentially diverting their traffic to your own site. Be cautious with this strategy, as it can lead to higher CPCs, but the payoff can be significant in terms of gaining new customers.
Real-Life Example: HelloFresh, a meal kit delivery service, targeted competitor keywords such as “Blue Apron meal kits” in their Google Ads campaigns. By bidding on their competitors’ brand terms, HelloFresh was able to capture traffic from users who were initially searching for rival services.
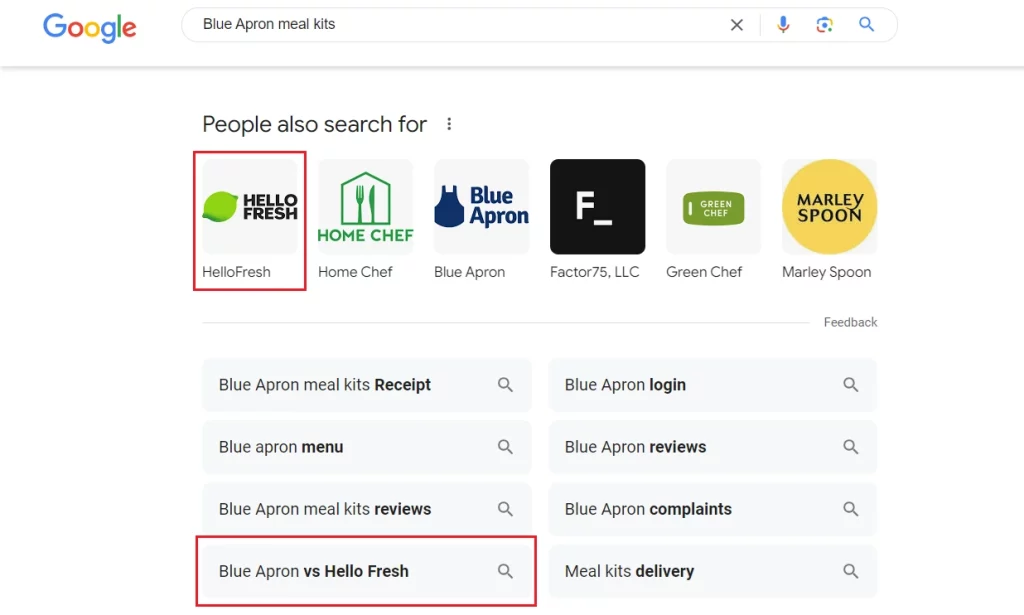
What They Did Well: HelloFresh capitalized on the intent of users looking for meal delivery services but remained open to alternatives. Their ads emphasized what set them apart from the competition, such as unique meal options, flexibility in plans, and pricing. This helped convert potential Blue Apron customers into HelloFresh subscribers.
Outcome: HelloFresh saw a 30% increase in click-through rates (CTR) on competitor-branded ads, resulting in a significant lift in new customer sign-ups. Targeting competitor keywords allowed HelloFresh to capture an audience already inclined toward their product category, leading to higher conversion rates and lower acquisition costs compared to broader targeting.
#6 Leverage Customer Data for Personalized Marketing
Using customer data to create personalized marketing campaigns can significantly improve engagement and conversion rates. By segmenting your audience based on previous behaviors (such as browsing history or past purchases), you can tailor ads to their specific needs, leading to higher relevance and better results.
Real-Life Example:
Zappos, an online shoe and clothing retailer, uses customer data to create personalized product recommendations across email, search, and display ads. By analyzing user behavior and purchase history, Zappos ensures their ads are highly relevant and personalized.
What They Did Well:
Zappos’s personalized recommendations are powered by deep insights into customer behavior. Their ability to tailor ads and recommendations based on user preferences creates a more engaging and effective marketing experience.
Outcome:
Zappos’s personalized marketing strategy drives a significant portion of its repeat sales, demonstrating the power of using customer data to deliver highly relevant ads and recommendations.
Best Types of Google Ads for Ecommerce
When running an ecommerce business, choosing the right type of Google Ads is crucial to driving traffic and boosting sales. Each ad type offers unique benefits that can help you reach your target audience more effectively. Let’s have a look at the best types of Google Ads for ecommerce, detailing how they work and why they’re beneficial for your online store.
Shopping Ads
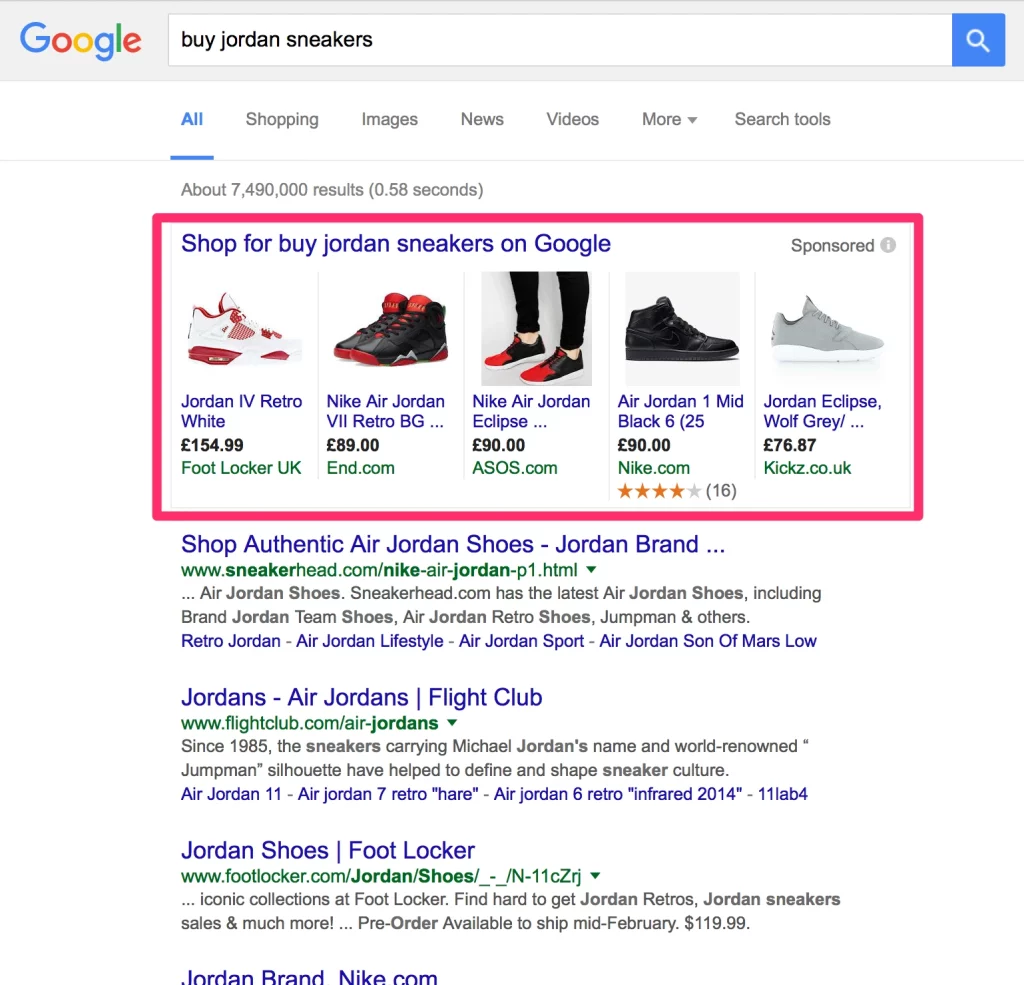
Google Shopping Ads are a game-changer for ecommerce businesses. Unlike other ad types, Shopping Ads visually showcase product images, prices, and store names directly within the search results, making them highly engaging and informative for users.
What makes Shopping Ads preeminent is their conversion power—the conversion rate for this ad type ranges from 0.83% to 3.30%, depending on the industry. The visual appeal combined with key product information upfront simplifies the decision-making process for buyers, making these ads highly effective for driving sales.
Compared to Search Ads, Shopping Ads provide a richer user experience by showing product details before users even click, making them particularly beneficial for ecommerce models like dropshipping.
Search Ads
Google Search Ads remain a cornerstone of paid advertising and are the most versatile option for ecommerce businesses. Unlike Shopping Ads, Search Ads focus on targeting specific keywords that your potential customers are actively searching for. Appearing at the top of the search results page, they provide unmatched visibility for users who are ready to buy.
One key advantage of Search Ads is their flexibility in targeting intent-based searches, leading to 35% of product searches converting into purchases within five days. While Shopping Ads excel in showcasing products, Search Ads win by precisely targeting customers who are already searching for solutions or products similar to yours. They are especially advantageous for businesses aiming to capture high-intent traffic.
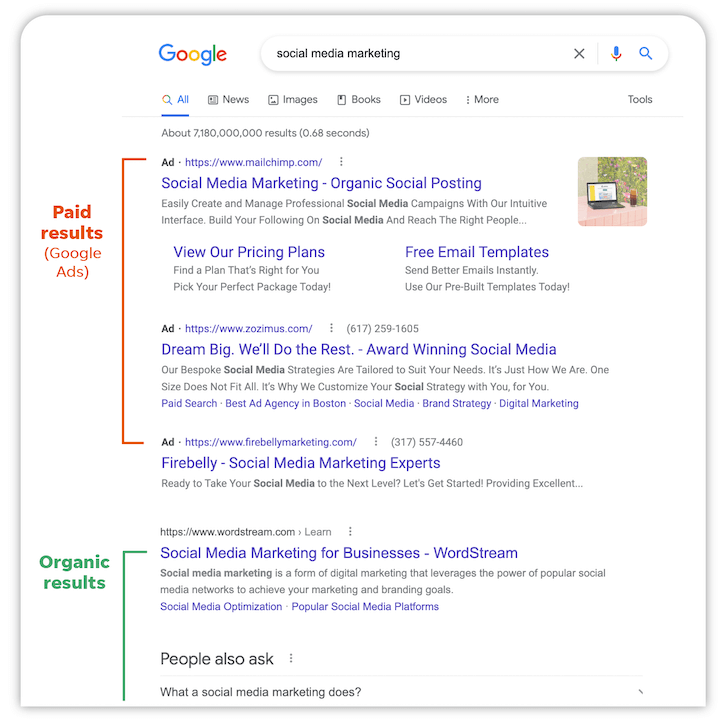
Display Ads
Google Display Ads shine in areas where traditional Search or Shopping Ads may not: brand awareness and retargeting. These visually engaging ads are displayed across Google’s vast Display Network, which reaches millions of websites. Unlike other ad types, Display Ads allow businesses to craft visually creative content to keep your brand top-of-mind with users. They are especially valuable for retargeting users who have visited your site but didn’t make a purchase.
While Shopping and Search Ads focus more on immediate conversions, Display Ads are perfect for reinforcing brand presence and gently nudging potential buyers over time. Display Ads also offer detailed targeting options, including user behavior and demographics, giving you more control over who sees your ads.
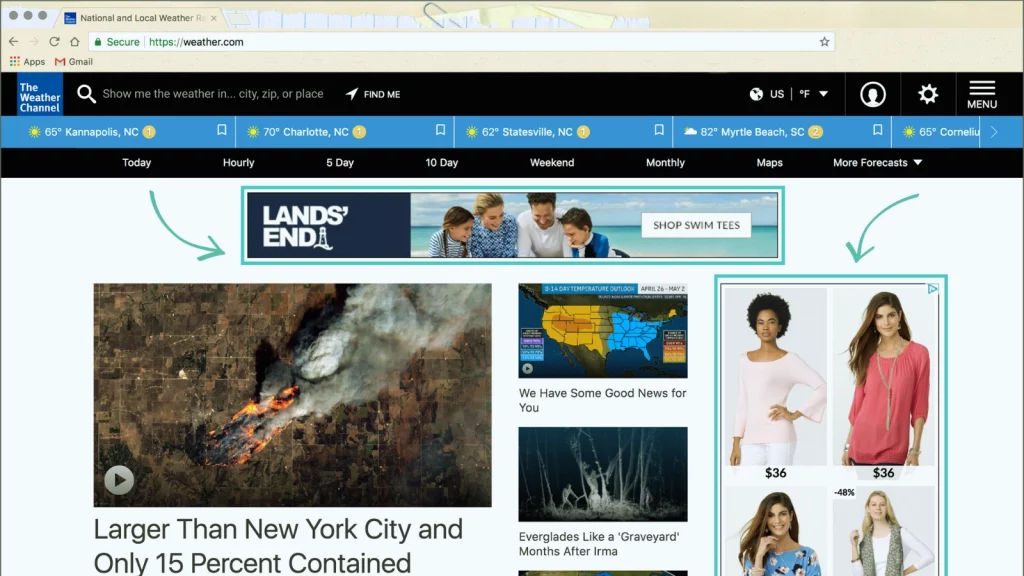
Video Ads
Google Video Ads, primarily served through YouTube, offer something that other ad types cannot—emotional engagement. With over 2 billion logged-in users each month, YouTube provides a massive platform for ecommerce businesses to tell their stories and build deeper connections with their audience. Video Ads excel at brand storytelling, driving long-term customer loyalty and emotional responses that often lead to purchasing decisions.
Compared to Display or Search Ads, Video Ads stand out for their ability to showcase your products in action and convey your brand message in an immersive way. While they may require more investment, their power to create brand engagement through visual storytelling makes them irreplaceable for businesses aiming to stand out in competitive markets.
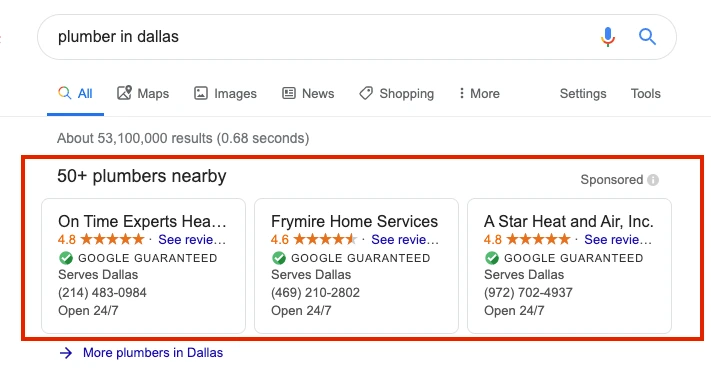
Local Services Ads
For ecommerce businesses with physical store locations, Local Services Ads (LSAs) offer a unique advantage by bridging the gap between online and offline. LSAs are triggered when users search for services or products near their location, helping businesses capture local traffic. This ad type is especially beneficial for businesses looking to attract local customers to their physical stores while still maintaining an online presence.
Unlike Shopping and Search Ads, which focus on online sales, LSAs give businesses the flexibility to drive foot traffic to stores, making them ideal for businesses that rely on both ecommerce and in-person sales.
Key Metrics to Track in a Google Ads Strategy for Ecommerce
Tracking the right metrics is essential to optimizing your Google Ads campaigns for ecommerce. Each metric offers valuable insights into different aspects of your campaign’s performance, allowing you to make data-driven decisions that drive better results. Here are the most important metrics to monitor, and how they work together to maximize your ecommerce success:
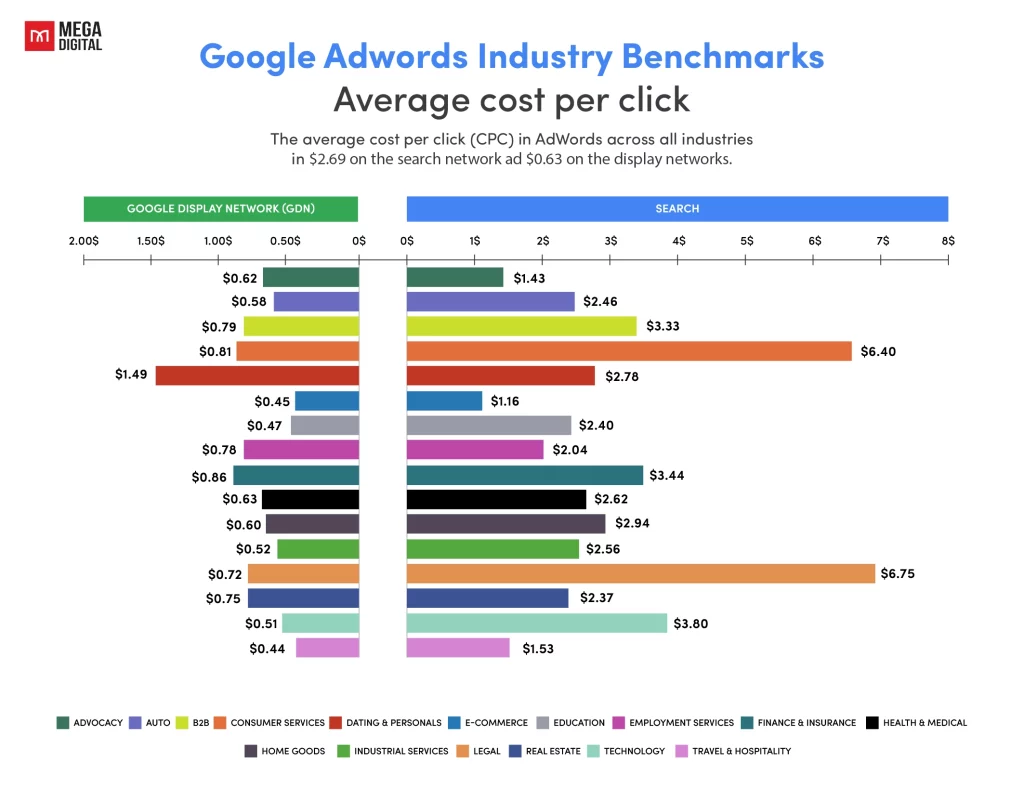
CPC (Cost per Click)
CPC measures the amount you pay for each click on your Google Ad. Managing CPC is crucial in ecommerce, where high clicks can lead to increased costs without necessarily driving sales. The average CPC for ecommerce in Google Ads is $1.16 for Search ads and $0.45 for GDN ads, but this varies by industry and keyword competitiveness. Monitoring and optimizing your CPC ensures you’re getting the most qualified traffic for your budget.
While lower CPC is beneficial, quality matters more. A low CPC that doesn’t convert into sales can waste your ad spend, which makes balancing cost and quality traffic essential.
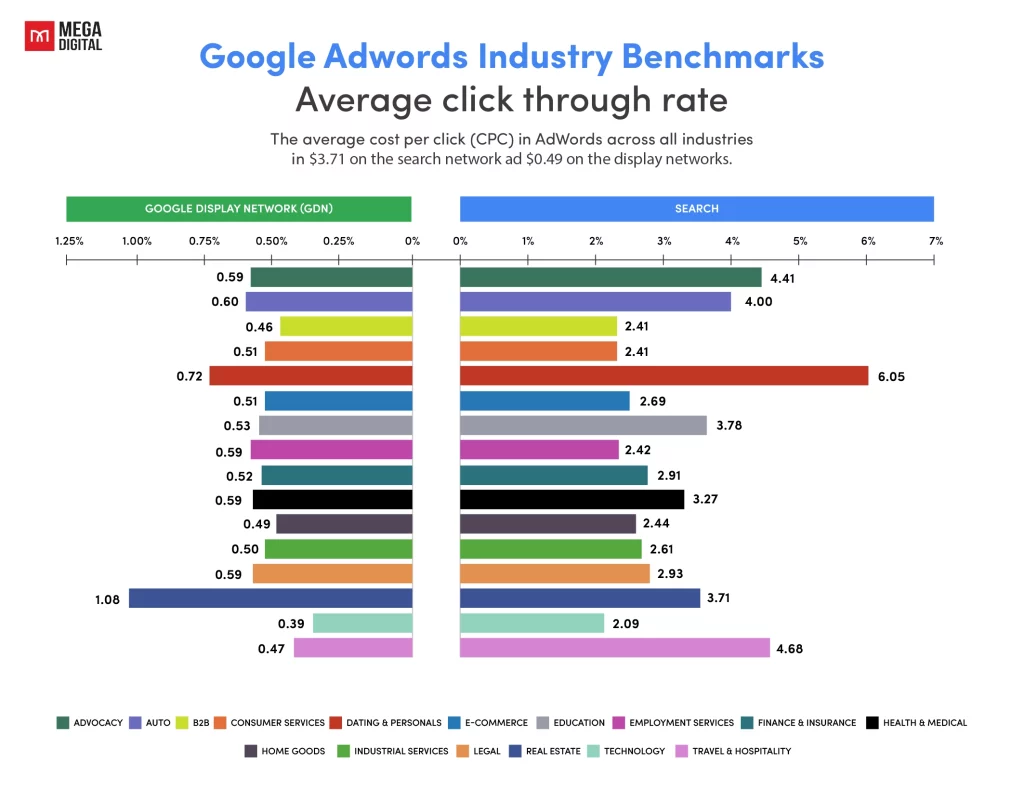
CTR (Click-through Rate)
CTR measures the percentage of users who clicked on your ad after seeing it. For ecommerce businesses, a high CTR indicates that your ads are relevant and engaging to your target audience. Google Ads reports that the average CTR for ecommerce is around 2.69% for Search ads and $0.51 for GDN ads, but top-performing campaigns can achieve significantly higher. A high CTR improves your Quality Score, which can lower your CPC and enhance ROAS.
If your CTR is low, it suggests that your ads aren’t resonating with potential customers or that your keywords may not be aligned with user intent. By improving CTR through better ad copy and more relevant keyword targeting, you not only attract more clicks but also improve your Quality Score, which can lower your CPC and improve ROAS.
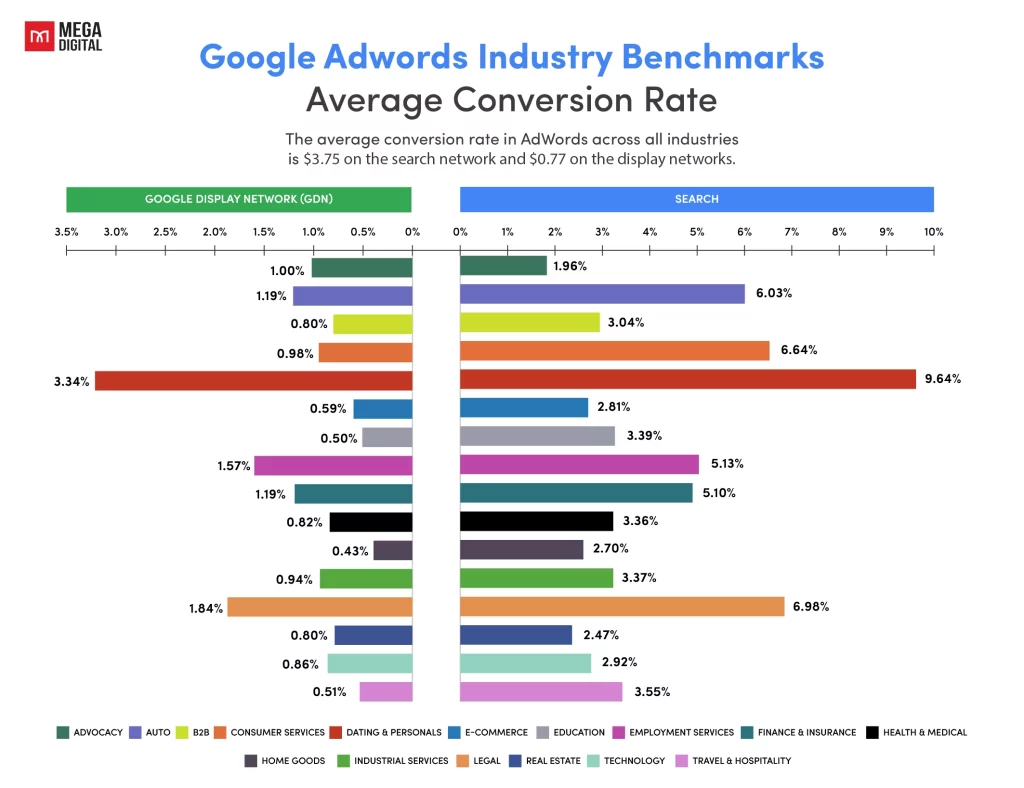
CVR (Conversion Rate)
CVR measures the percentage of users who complete a desired action, such as making a purchase, after clicking on your ad. In ecommerce, CVR is one of the most important metrics, as it directly impacts sales. The average CVR for ecommerce falls around 2.81% (Search ads) and 0.59% (GDN ads). If your CVR is lower than industry standards, it may signal issues with your website experience, product pricing, or the relevance of your landing pages.
Optimizing CVR is essential for turning clicks into conversions. High CVR combined with efficient CPC and strong CTR leads to better ROAS and overall campaign success.
ROAS (Return on Ad Spend)
ROAS calculates the revenue generated for every dollar spent on ads. Maintaining a positive ROAS is critical for ecommerce businesses, as it directly affects profitability. A benchmark study found that the average ROAS for Google Ads in ecommerce is between 200% and 400%, meaning you should aim to generate $2 to $4 in revenue for every $1 spent. Improving ROAS requires focusing on attracting high-intent traffic, refining landing pages, and matching ad copy to user search intent.
Maximizing ROAS means more efficient ad spend and higher revenue generation. Reducing CPC while maintaining a high conversion rate can significantly improve ROAS. A good ROAS means your ad campaigns are not only driving traffic but also encouraging conversions, leading to higher revenue.
In summary, by tracking and optimizing metrics like CPC, ROAS, CTR, and CVR, ecommerce businesses can pinpoint the exact areas that need improvement in their ad campaign. A comprehensive Google Ads strategy should focus on attracting qualified traffic, lowering ad costs, and converting clicks into sales. Monitoring these key metrics together helps create a feedback loop that drives growth and profitability, ensuring long-term success for your ecommerce store.
Final Word
Google Ads for ecommerce offers immense potential for driving traffic and conversions. By leveraging the right ad types, creating targeted campaigns, and continually optimizing based on performance, ecommerce businesses can maximize their returns and achieve long-term success. Plus, don’t forget to keep an eye on key metrics such as CPC, ROAS, and CVR to ensure your campaigns remain profitable.