In the world of online selling, honesty is the best policy, especially when it comes to running Shopping ads. Google Merchant Center misrepresentation suspension can lead to account troubles. So, keep it straight, truthful, and clear. Correct any misrepresentations, follow Google’s rules, and you’ll be on the path to success in the online marketplace.
What does Google Merchant Center misrepresentation warning mean?
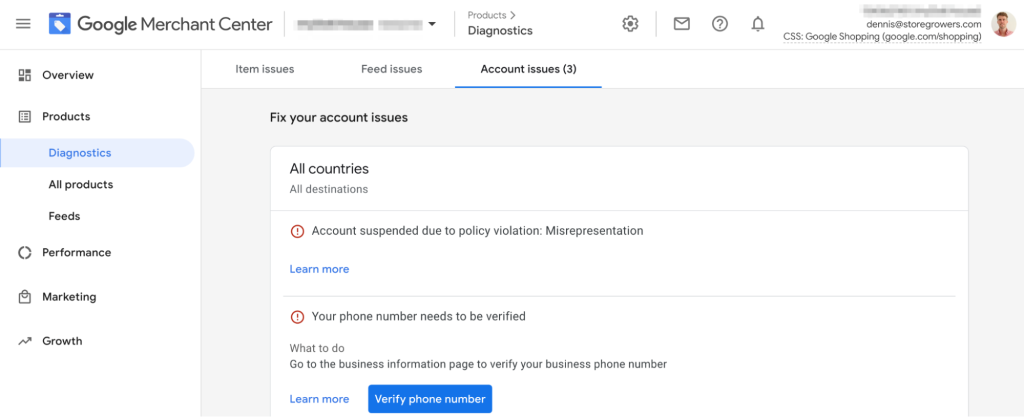
Definition: This message is a warning for Google Merchant Center account suspension. It means that Google suspects that your business or product information is not accurate or honest. If you receive this warning and don’t address the issue, your Google Merchant Center account could be suspended.
How to know: You might come across a notification in your Google Merchant Center (GMC) or receive an email resembling this: “Account suspended due to policy violation: Misrepresentation of self or product (untrustworthy promotions)”.
Mega Digital has encountered such issues frequently when running ads for over 2000 customers, and here are the most common causes we come across.
Causes & how to fix “Misrepresentation of self or product”
If you’ve found yourself facing the daunting challenge of Google Merchant Center suspended for misrepresentation, you’re not alone. Google’s commitment to maintaining trust and transparency in online commerce means strict policies are in place, and violations can result in account suspensions.

1. Omission of relevant information
“Omission of relevant information” means not telling or forgetting to tell important stuff when you’re talking about something. This can occur intentionally or unintentionally. Leaving out important details can cause confusion or misunderstandings, and severe Google Merchant Center misrepresentation problems.
How to know if you leaving out relevant information
- Not clearly explaining the payment
Failing to provide clear information about the charges and overall expenses to users both before and after their purchase.
The price of things may change based on different factors like auctions, membership fees, contracts, payment plans, or extra things you have to buy, and this can add to the cost. To follow the rules, check the Product data specifications for advice on how to do this right.
- Not explaining related conditions
Neglecting to clarify all the crucial information before and after a purchase.
This can include not telling customers about your terms and conditions, shipping info, or making it hard to find your return and refund policy.
- Leaving out important details
Omitting vital information when advertising as support for charitable or political causes.
This means showing charity or tax exemption numbers for donations and saying whether political donations are tax exempt or not.
Solution for omission of relevant information
- Check pricing:
Ensure your pricing is accurate, including any taxes or shipping fees. You can update this information in your Merchant Center settings or product feed. Make sure the prices in your product feed match those on your website.
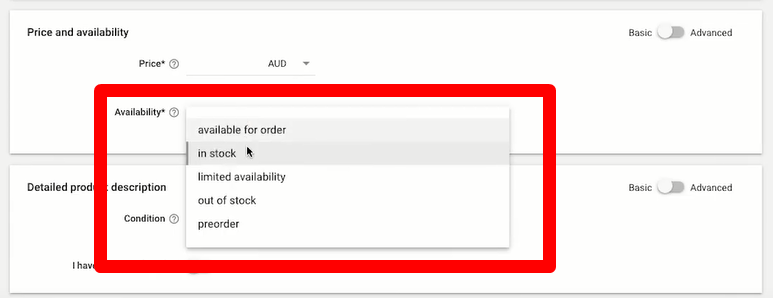
- Use automatic item updates:
If you have trouble updating prices or availability or can’t create a dynamic data feed, consider turning on Automatic Item Updates in the Merchant Center. Be aware that this triggers a website crawl by Google, which usually takes about three days. It’s not a long-term solution for frequently changing data. If too many items don’t match between your website and product feed, your account may be suspended.
- Correct product URLs:
Ensure your product URLs correctly link to the right products.
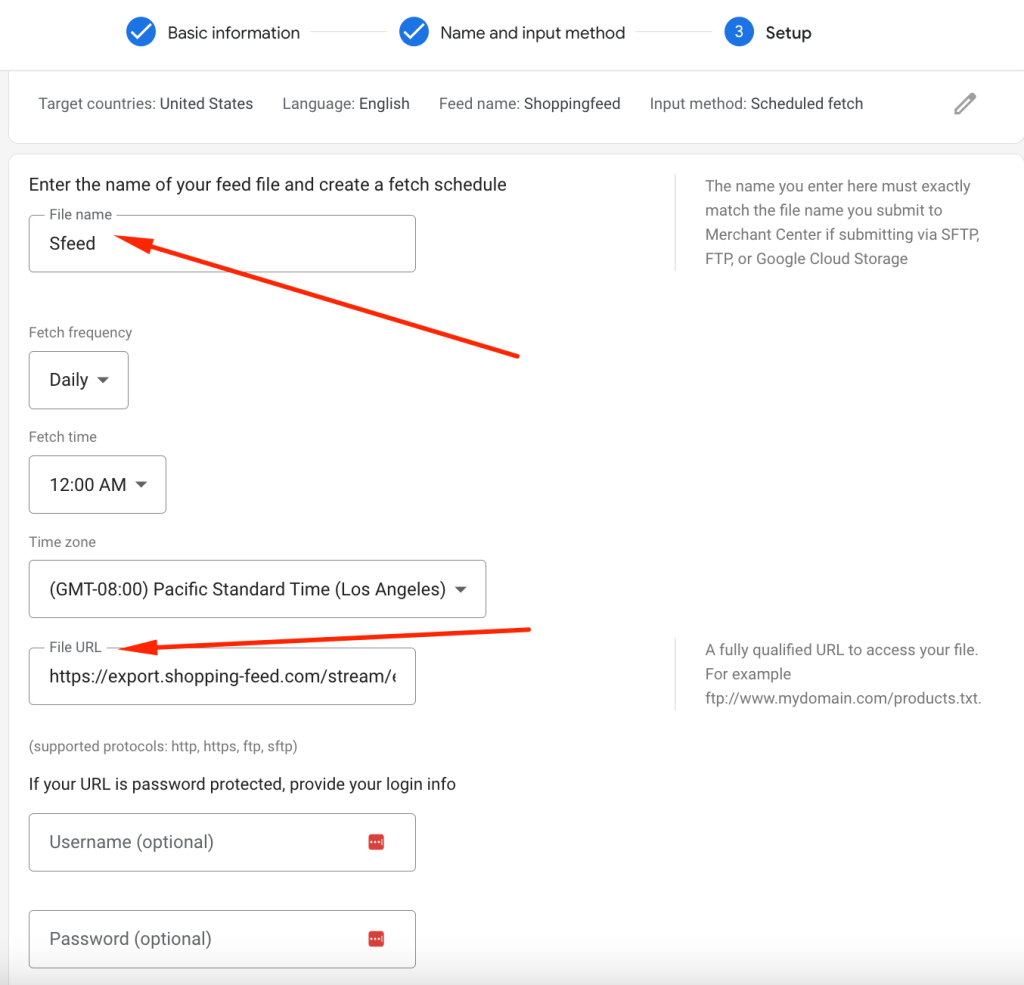
For instance, if you sell mattresses in different sizes but all links lead to one size, Google may get the wrong price. Make sure your structured data markup is accurate, so Google can read the price and availability for each item.
- Clarify product descriptions:
Clearly communicate what customers are buying. If, for example, you sell boxing gloves individually, make it evident that the purchase is for a single glove.
- Display important information:
Ensure your website prominently displays relevant information. Update and explain your refund or returns policy clearly. If you sell products benefiting charities or political causes, include the charity or tax exemption number, and if purchases are tax-deductible, clearly disclose this on your website.
2. Unavailable promotions
“Unavailable promotions” typically refer to marketing or promotional offers that are not accessible or cannot be redeemed by customers as advertised. This could happen if the products or services mentioned in the promotion are out of stock, unavailable in certain locations, or if there are other limitations preventing customers from taking advantage of the offer.
How to know if you’re promoting unavailable products or deals
Advertising items that are not in stock, promoting expired deals, or urging actions in an ad that can’t be easily done from the webpage. For detailed guidance on following this rule, refer to the Product data specification attributes regarding availability and price.
Solution for unavailable promotion
- Update product availability:
Ensure you regularly update product availability, if an item is out of stock on your website but still advertised, it could lead to issues.
- Use an inventory threshold to prevent overselling:
If you sell across multiple channels, consider using an inventory threshold to prevent overselling. For example, if you use platforms like Shopify, Amazon, and Walmart, set rules to handle low stock. If stock falls below a certain level for a specific product, mark it as “out of stock” on platforms like Amazon and Walmart.
- Check the accuracy of your structured data on product pages:
Sometimes, Google may only read the regular prices from your webpage, even if you’re displaying sale prices in your ads. This mismatch can trigger warnings.
- Avoid discrepancies in price values:
Some issues can arise when websites use JavaScript for schema coding or update prices on product landing pages using JavaScript. Google recommends scheduling regular feed uploads or updates via the Content API immediately after making changes to product prices on your website.
3. Misleading or unrealistic promotions
“Misleading or unrealistic promotions” means deceptive marketing that tricks customers with false or unlikely claims, leading to confusion or disappointment. This type of Google Merchant Center misrepresentation can include promising unreal results or exaggerated benefits, and violating advertising rules.
How to know if you’re promoting misleading or unrealistic promotions
- Provide incorrect information
Offering incorrect information about who you are, your qualifications, or the product you’re promoting.
Examples: Saying you’re an authorized seller when you’re not, using a well-known brand to attract attention to a different product on your website.
- Make false statements
Using false statements or making unrealistic claims to lure users into believing unlikely outcomes.
Examples: Advertising “miracle cures” for medical conditions or extreme weight loss products that promise results that are hard to believe.
- Suggest false connection or endorsement
Falsely suggesting a connection or endorsement from someone or something else.
Examples: Misleadingly imitating official government websites or using official-looking seals, and suggesting a link with a person, organization, product, or service that doesn’t exist.
- Promote harmful health content
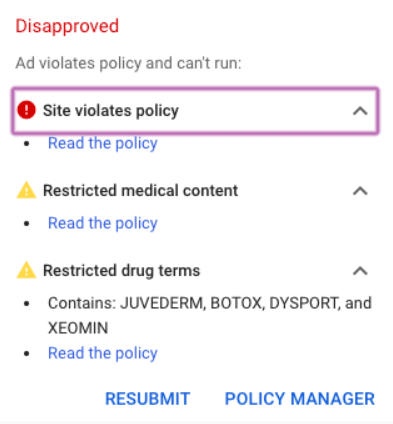
Promoting content that makes harmful health claims or contradicts established scientific consensus, especially related to significant health crises.
Examples (not an exhaustive list): Advocating against vaccines, denying the existence of conditions like AIDS or Covid-19, or promoting gay conversion therapy.
- Make provably false claims
Making claims that are provably false and could seriously harm people’s trust in electoral or democratic processes.
Examples (not an exhaustive list): Spreading misinformation about voting procedures, the eligibility of political candidates based on age or birthplace, election results, and false reports of public figures’ deaths, or accidents.
- Share opposed widely accepted climate change scientific findings
Sharing content or claims that go against widely accepted scientific findings on climate change.
Climate change is a global crisis with far-reaching implications for the environment, ecosystems, economies, and human societies. The overwhelming consensus among climate scientists is that human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation, are the primary drivers of climate change.
Solution for misleading or unrealistic promotions
- Review product descriptions:
Carefully check your product descriptions for any banned keywords or claims. Mega Digital can assist by eliminating over 4,000 keywords not permitted by Google Shopping.
- Avoid exaggerated claims:
Avoid exaggerating the benefits of your product. Don’t make promises of miraculous cures or guarantees that don’t match your product category.
For instance, while Google may permit certain weight-loss claims for diet programs or workout equipment, you can’t make the same claims for products like nail polish. If you do guarantee results, ensure you have a clear return and refund policy on your page.
- Avoid false affiliation:
Don’t suggest any affiliation with organizations or businesses you aren’t part of. Avoid claiming to be a certified or licensed business if you’re not, and don’t pretend to be associated with or endorsed by an entity or organization when it’s not true.
- Avoid harmful content:
Avoid including content that makes harmful health claims or contradicts established scientific consensus. These are strictly prohibited.
4. Unacceptable business practices
“Unacceptable business practices” are actions by a business that break ethical or legal rules, like fraud or unfair competition. These actions can harm a business’s reputation and lead to Google Merchant Center misrepresentation issue.
How to know if you’re promoting unacceptable business practices
- Give false information about the business or product
Note: Google may check various sources, including promotions, websites, accounts, and third-party sources, to determine if a seller or website is not trustworthy.
Examples: Deceiving users into giving money or information with unclear or untrue reasons; pretending to be someone else, using a fake business name, or providing incorrect contact details; charging users for items that are usually free; websites trying to steal user information (phishing).
- Hide or distort important information
Deceiving users by hiding or distorting information about the seller’s business, product, or service.
Example 1: Pretending to be well-known brands or companies by using or changing their content in ads, URLs, or other places, or acting like you are that brand or company in interactions with users.
Example 2: Tricking users into giving money or information through a fake business that doesn’t have the qualifications or ability to provide the things they advertise.
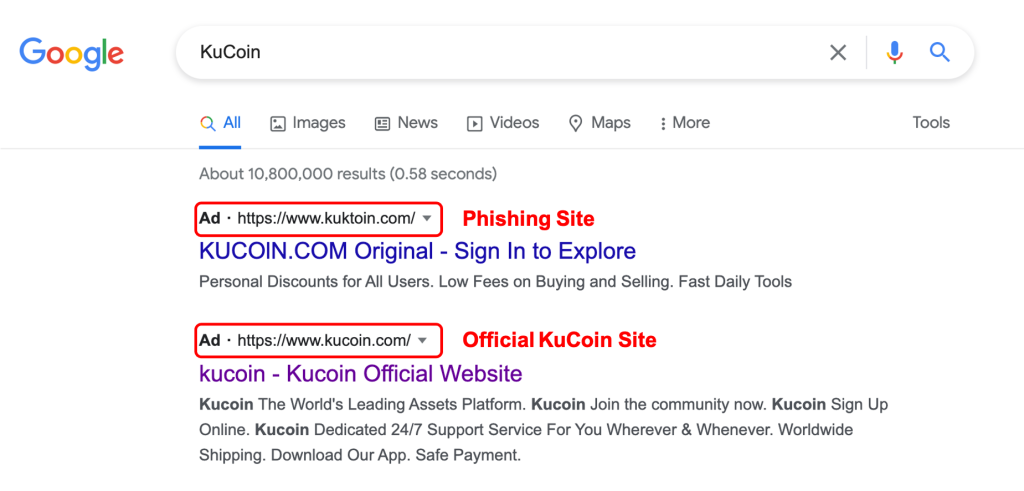
- Use “phishing” methods
Websites that use “phishing” methods to collect user information.
Examples: Websites that fool users into revealing their personal information by pretending to be a trusted store or company.
Solution for unacceptable business practices
- Show the right information:
Never provide false information about your business or products. Honesty is key to building trust with your customers.
- Provide clear & accurate information:
Ensure that all information about your business, products, and services is clear, accurate, and up-to-date. Misleading or incomplete details can lead to confusion and distrust.
- Avoid hiding information:
Do not engage in deceptive practices like hiding or distorting information. Be straightforward about who you are, what you offer, and how your products or services work.
- Protect user data:
Never use “phishing” methods to collect user information. Respect user privacy and follow proper data protection practices to safeguard sensitive information.
Final word
To sum it up, fixing Google Merchant Center misrepresentation issues is important for getting your account back on track and for maintaining trust in your online business. By following the advice given here, you can correct these issues, play by Google’s rules, and keep growing your online business honestly.