Users are clicking but leaving too soon? That’s a clear sign your content isn’t holding attention. One thing you can do to solve this is to boost the Average Time on Page metric. In this guide, we’ll walk marketers through what Time on Page GA4 is and share practical strategies to keep visitors engaged longer!
What is Time On Page in GA4?
In Universal Analytics (UA), the Average Time on Page shows the average amount of time people stayed on a specific page of your website. This metric was used by marketers to determine how engaging their content is and also this would be used to gauge whether the visitors got any value from it.
However, Google Analytics 4 (GA4) no longer uses this exact metric. Instead, it introduced something similar called Average Engagement Time. Although it is not a direct replacement, it lets you know how long a user actively interacts with your website or app.
To find this metric in GA4, go to the left-hand menu and click on “Reports”.
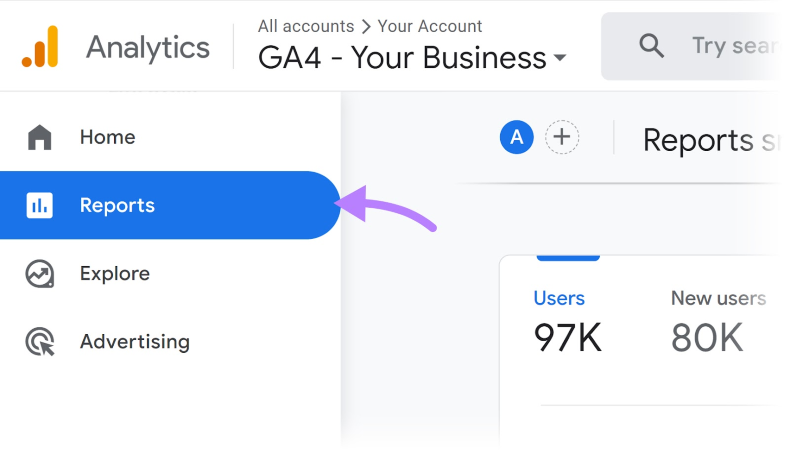
From there, navigate to “Life cycle” > “Engagement” > “Overview”.
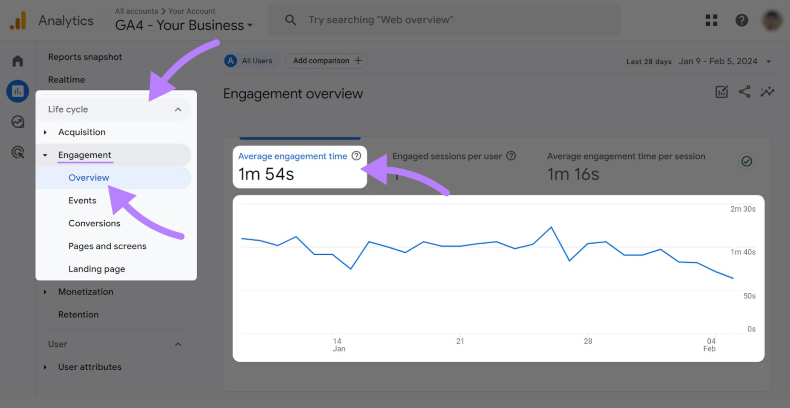
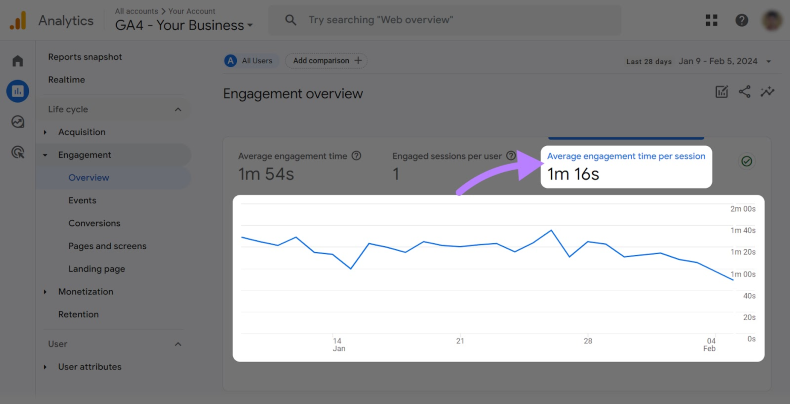
You’ll see the average engagement time for your whole website displayed there. This is the closest equivalent to the old “time on page” and helps you understand how long users are really sticking around.
Why Time On Page is a Crucial Metric?
Time on Page is more than just a number. It offers valuable insight into how well your content holds a visitor’s attention. Below are the key reasons why this metric matters for marketers:
1. Reflect Content Engagement Levels
Time on Page works like a signal for how well your content connects with visitors.
For example, if a blog post “How to set up GA4” keeps users on a page for more than 5 minutes, that is a strong sign that the content is useful and interesting. This insight helps you measure which pages are working well, so you can make more such content.
In contrast, if an article keeps users staying for only 5 seconds, this might indicate a need to change the tone, maybe even the structure or topic for other articles.
2. Evaluate the Quality of User Experience (UX)
When people spend more time on a page, it indicates a smooth experience, logical layout, and easy-to-follow content. In contrast, if users leave quickly, it may suggest confusion, poor navigation, or frustration with loading times.
Hence, the average time on page gives you a real-time reflection of the user’s experience. It’s a helpful way to spot areas that are working well and pages that may need UX improvements.
3. Imply SEO Performance
Time on Page has not been an official ranking factor, but it sure does relay messages about your content to search engines. A user usually sticks around long enough on a page because the page matches their search intent. Google then gets the hint, and the page will become relevant to the search query.

4. Correlate with Bounce Rate
Analyzing time on a page along with bounce rate can allow you to gain further insights for optimizing your pages. For example, if a page has a high bounce rate but users read for a considerable length of time, it may mean they found exactly what they need and do not have to click through elsewhere.
Hence, instead of assuming a high bounce rate is always bad, this combination helps you understand the full picture.
How To Calculate Average Time On Page?
To calculate the Average Time on Page, we divide the total amount of time users spend on a page by the number of page views where the users do not exit or bounce. In other words, we only count the pageviews when the users go to other pages of your site.
Let’s take a simple example. Suppose a landing page got 2,000 page views in a month and users spent 500 minutes on that page in total. Out of those views, 400 views were exits or bounces. So, the time on page in this case would be around 0.3 minutes.
It is noteworthy that GA4 does not exactly use this any longer. However, having a good understanding of its calculation adds great context for comparisons involving past performance or when migrating reports.
What Factors Affect Time On Page in GA4?
Several elements can influence how long visitors stay on a page. Let’s explore the key factors that affect time on page in GA4:
1. Content Quality
Content quality is one of the major factors affecting time on page. The main elements include:
- Relevance: Content that matches what users are searching for would hold their attention. When the content addresses needs or questions clearly, users would be much more likely to keep reading.
- Comprehensiveness: The detailed content analyzing thoroughly and covering all the key points would do much better than sketchy content that duplicates from other pages.
- Readability: Logical format makes the content easy to scan. Short paragraphs, headings, and bullet points facilitate pleasant reading and boost longer time on page.
2. Page Loading Speed
If a page takes too long to render, many visitors will leave without even viewing the content. Every extra second of delay can mean higher bounce rates and shorter sessions.
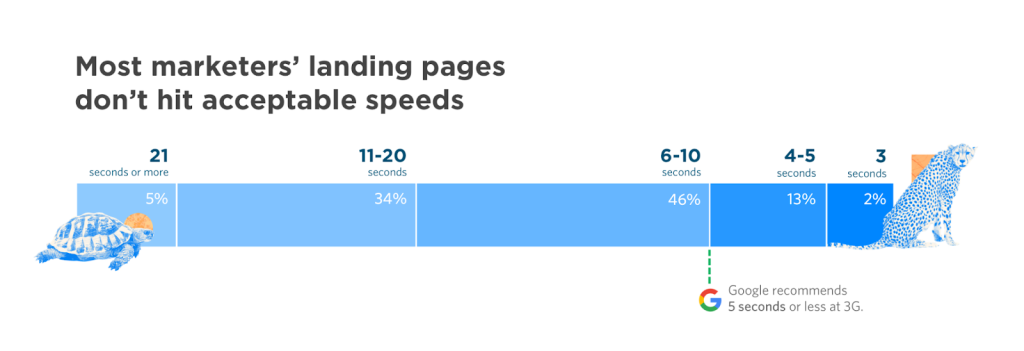
Besides, Google considers page speed a key component of user experience. A faster site not only keeps users around longer but may also perform better in search rankings.
3. Site Navigation
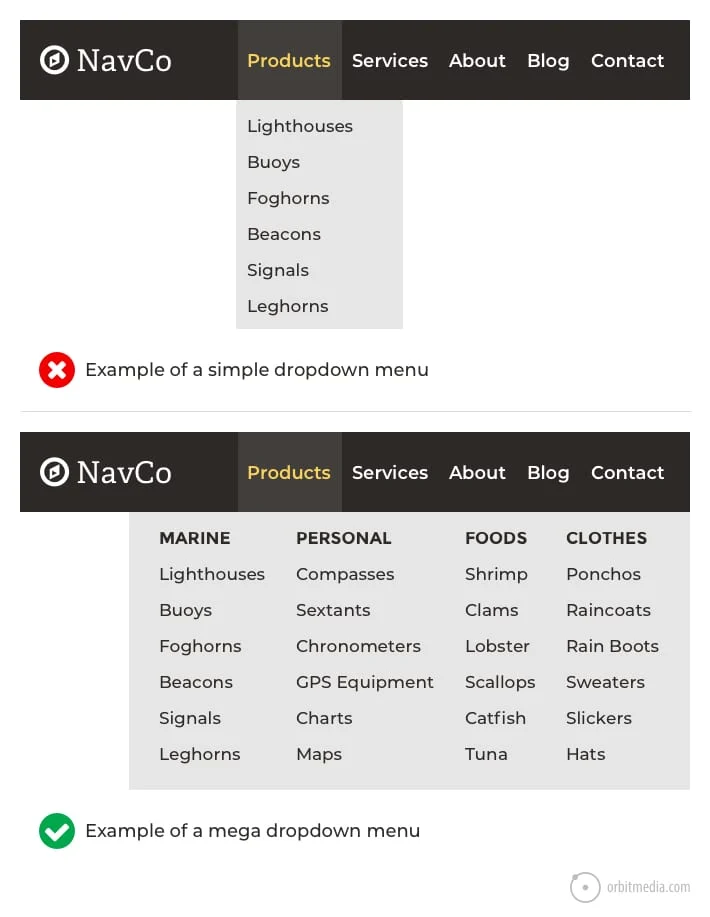
When visitors can easily find what they are looking for or switch between related pages, they will linger on your page. Otherwise, poor navigation may lead to confusion and early exits.
A well-constructed menu, internal links, and logical page hierarchy all add up to a better browsing experience and keep the users on your site longer.
4. Design & Visual Appeal
Good visual representation backs the content and keeps users on page for longer. White space, color consistency, legible typography, and appropriate imagery all serve a good user experience. On the other hand, cluttered layouts or outdated designs can drive visitors away quickly.
What Is a Good Time On Page in GA4?
A good average time on page in GA4 is evaluated depending on your website’s purpose, industry, and content types.
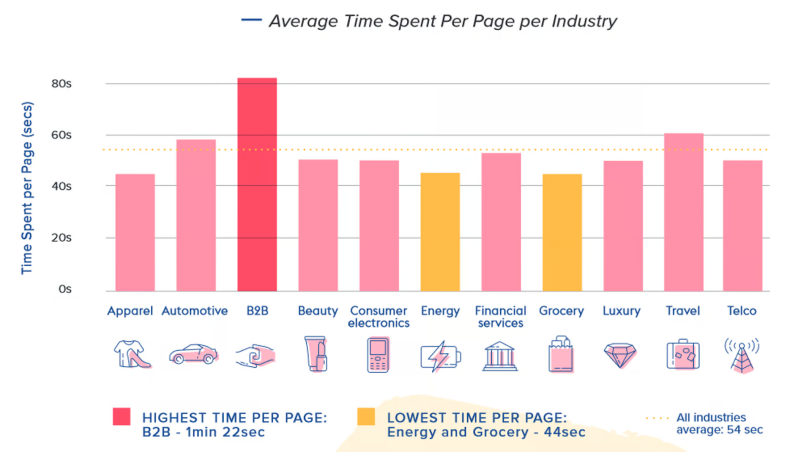
For example, if your page is a detailed guide, it’s reasonable for visitors to spend a longer time reading. On the other hand, if the page is just a quick how-to answer, even a 30-second visit might be perfectly fine.
It’s also important to compare your time on one page with other pages on your site. For instance, if after a long scrolling the page users are not taking any next steps like clicking to another page, you might need to rethink your CTAs.
How to Increase Your Average Time on Page?
If users are leaving your site too quickly, it could be a sign that your content or user experience needs improvement. Here are proven strategies to help increase your average time on page:
1. Create High-Quality Content
To keep users on your page, you need to make the content easy to read and truly helpful. Short paragraphs and subheadings should come with good formatting such as bullet points or numbering to improve the readability and flow.
The content format also matters. Some of the effective formats are:
- Listicles: Best for quick tips, steps, or recommendations.
- How-to articles: Ideal for outlining step-by-step instructions and thoroughly detailed explanations.
- Short-form articles: Great to include a very short news update or quick insight into a specific topic.
- Long-form articles: Ideal for complex subjects that probably need much more detail.
You can also mix and match these formats based on the topic and audience needs.
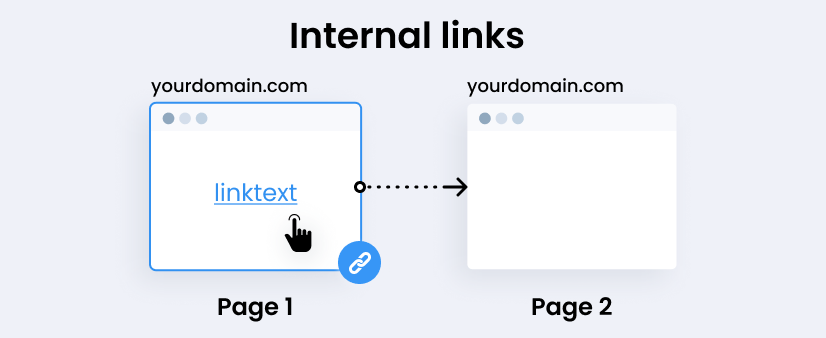
2. Use Internal Links
Internal linking is a simple yet powerful technique to retain users. It connects one page to another on your site to allow users to switch naturally from one topic to the next. Thus you are guiding users to explore more content that interests them.
For instance, when you publish an article on basic SEO techniques, link it to a post about advanced SEO tactics. This may stimulate interest among your readers to further explore other pages while applying what they have learned from reading the first article.
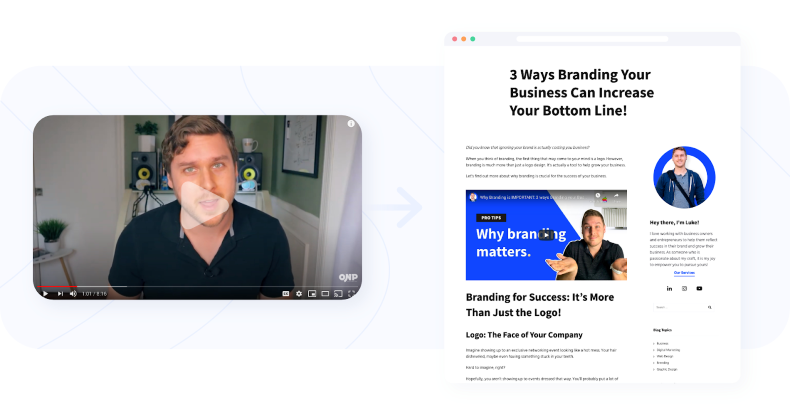
3. Add Multimedia
Adding multimedia elements can make your content easier to absorb. Images, videos, or infographics help break long walls of text and clarify ideas, which keeps readers continuing reading.
For instance, if a blog post is about branding for businesses, a brief tutorial video or step-by-step screenshots will help the readers follow along with the process more easily. Whenever a visitor watches a video or zooms in on a chart, they are naturally spending more time on that page.
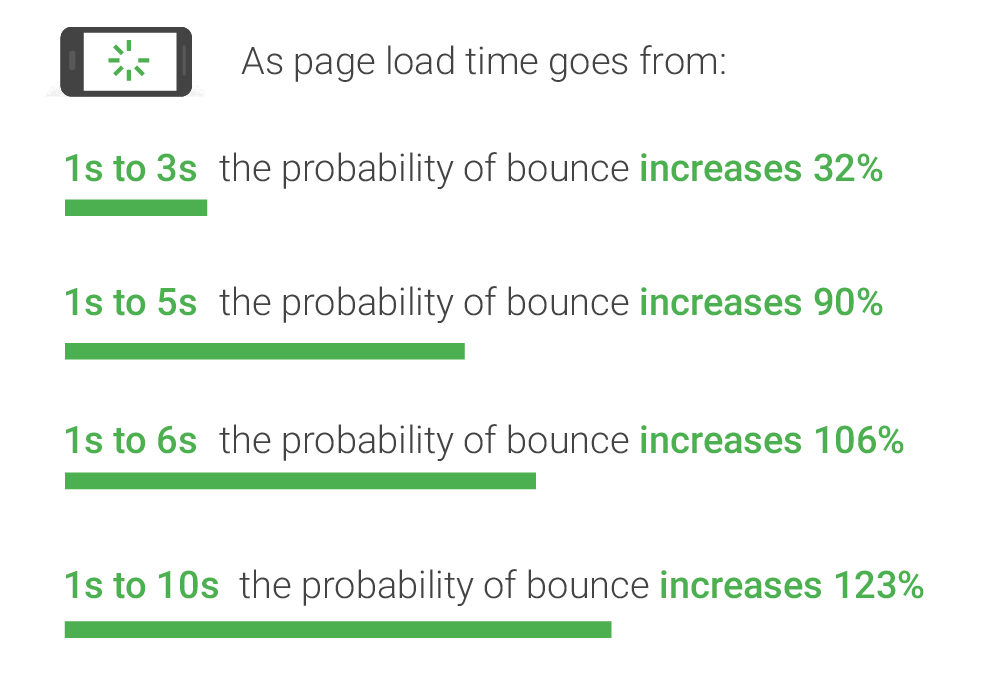
4. Speed Up Page Load Time
Page speed also contributes to how long visitors stay on your site. No matter how good your content is, users may bounce and look elsewhere if it takes too long to load. According to Google, the chances of a user bouncing away from a site sharply increase when load times rise from 1-3 seconds to 1-5 seconds.
To make your page load faster, you can compress images, enable browser caching, reduce HTTP requests, select a lightweight theme, and upgrade hosting. For example, if you run an eCommerce site, optimizing those large product images could help improve loading times.
5. Optimize for Mobile
Making your site mobile-friendly is key to keeping users engaged as mobile traffic continues to rise. Here’s how to do it effectively:
- Keep navigation simple: Use a clean menu so users can quickly find what they need.
- Make buttons and links touch-friendly: Ensure they’re large enough to tap without zooming.
- Use readable text sizes: Avoid making users pinch to zoom. Make sure fonts are clear and legible on smaller screens.
- Break content into short paragraphs: Long blocks of text can be overwhelming on mobile, so use white space wisely.
- Test on multiple devices: Check how your site looks and works on different phones and screen sizes to catch any issues.
Wrap Up
Improving time on page in GA4 isn’t just about keeping users around longer. It’s about delivering value, enhancing user experience, and guiding visitors toward meaningful actions. Start optimizing today, and turn every second into a stronger connection with your audience.